process safety management (PSM) services
Process Risk consultants have provided full support in all aspects of the OSHA’s Process Safety Management standard (29 CFR 1910.119) for clients in all industries since the regulation was introduced. Our world-wide experience in safety and risk management over the past 35+ years is on display when we address several of the common aspects of RMP including PHAs, Management of Change (MOC), operating procedures, training, mechanical integrity and auditing to mention a few. Refer to some of the most common services links below for additional details.
Process Safety Management (PSM) Program Development
Companies handling highly hazardous chemicals in excess of threshold quantities must comply with OSHA’s Process Safety Management (PSM) standard, 29 CFR 1910.119 as well as related state level programs. Read More
PSM / RM Program Enhancement and Optimization
Leverage your existing program to help create a state of the art program that meets the latest guidelines and requirements. Incorporate best industry practices to .... Read More
PSM / RMP Compliance Auditing
OSHA PSM and EPA RMP regulations include a requirement to perform compliance audits every 3 years. Our compliance auditng services can address all regulatory or internal company auditing requirements. Our experienced staff helps identify both compliance deficiencies as well as opportunities to optimize the effectiveness of your safety programs. Read More
Process Hazard Analysis (PHA)
Hazard identification and analysis uses team knowledge, checklists of hazards and process information to determine process, and facility characteristics that could pose safety or environmental hazards that can lead to undesirable consequences. Read More
Procedure Development and Enhancement
Written procedures are required for many activities in a process such as operations and maintenance. Many companies assume their employees can write procedures simply by documenting what they do. However, this approach often produces ineffective procedures. ... Read More
Mechanical Integrity
A complete Mechanical Integrity (MI) program is required by the PSM and RMP regulations and is intended to ensure equipment does not fail in a way that causes or affects a release of highly hazardous chemicals. MI covers the design, fabrication, construction / installation, and operation of equipment throughout the entire process life cycle. All maintenance, inspections and testing is included along with the associated training and procedures. Read More
Management of Change (MOC) - Process and Organizational
OSHA PSM and EPA RMP requires Management of Change procedures to ensure hazards associated with the process changes are fully managed and comply with industry codes, standards and recommended practices. It assists in controlling risks to the public, employees and the environment; minimizes business interruption. Read More
Safety Instrumented Systems (SIS)
ANSI/ISA-S84.00.01-2003, (IEC 61511 Mod), Application of Safety Instrumented Systems for the Process Industries, (called IEC 61511 / ISA 84 here) addresses the application of Safety Instrumented Systems (SIS) ds are needed... Read More
Layers of Protection Analysis (LOPA)
LOPA is considered a more quantitative risk assessment method than a PHA study. It provides an objective, rational and reproducible method of evaluating the risk of hazard scenarios and comparing it with risk tolerance criteria. It is often linked to the results of an associated PHA study. Read More
Safeguard Protection Analysis (SPA)
Safeguards protect processes from process safety incidents. They are critically important and consequently, every effort must be exerted to ensure they are functional, effective, and adequate. A focused review of identifed safeguards is now required in certain US regulations. Read More
Inherently Safer Technology (IST)
Inherently Safer Technology (IST) can enhance overall chemical safety and security risk management programs. This concept has become a requirement in select state regulations as well as gaining exposure throughout all industries. Benefits can be realized from new projects to existing processes. Read More
Human Factors Review and Analysis
Human factors are considerations that can impact any operation or the performance of any trained staff. People are key components to the safe operation of industrial processes. They are involved in process design, operation, maintenance, etc. Identifying factors that can adversely impact human operation is key to having a well managed safety program. Read More
NEP Compliance Support - Select Industries
National Emphasis Programs (NEP) have been established in several industries. These programs place additional demands on various aspects of process safety management to enhance management of risks from catastrophic events in processes involving toxic... Read More
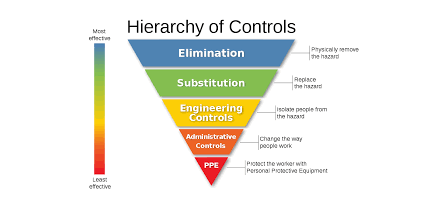
Hierarchy of Controls Analysis (HCA)
Various types of controls are used in process safety management to manage the risks of catastrophic events in processes involving highly hazardous materials. Certain types of controls provide a more reliable means of controlling risk than others. A review of all control options is a more recent expectation in some state regulations and best practices. Read More
Emergency Response Programs
Emergency Response Programs (ERPs) are required and an essential element of process safety and risk management programs. Most facilities have ERPs established however opportunities to update or optimize them may be present for companies in all industries. Read More
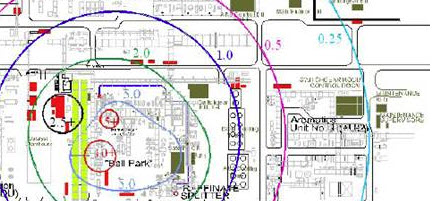
Facility Siting & Consequence Modeling
OSHA PSM and EPA RMP include requirements to address facility siting. Facility siting is comprised of several components tied to PHA studies as well as full site consequence modeling including building evaluation, consequence analysis and building risk assessment for the site. Read More
Incident Investigation
OSHA PSM and EPA RMP require covered facilities to investigate defined incidents. These incidents may include near miss events and root cause analysis. Maximize the learning value from previous incidents and utilize the information to enhance your safety program(s). Read More
Quantitative Risk Assessment (QRA)
Various types of controls are used in process safety management to manage the risks of catastrophic events in processes involving toxic... Read More
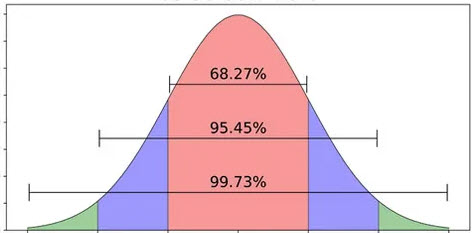
Probability Modeling
Companies are sometimes faced with the possibility of catastrophic accident consequences and need to assess their likelihood to determine what remediation may be necessary.... Read More
Simultaneous Operations (SIMOPS) Review
Simultaneous operations (SIMOPs) are situations where two or more operations or activities occur at the same time and place in a facility.... Read More
Safety Management Systems
Process Risk developing formal management systems, implementing them, and assisting companies to self-verify compliance or to seek certification. This includes ISO 9000, 14000, OSHAS 18000, ISO 27001, ISO22301, and ACC Responsible Care™... Read More
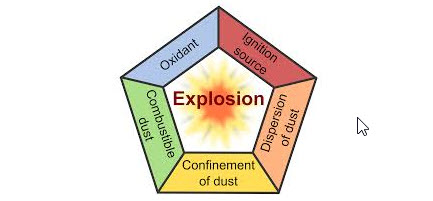
Dust Hazard Analysis and Management
NFPA 652:2016, Standard on the Fundamentals of Combustible Dust, requires that a safety management system (SMS) address the hazards of combustible dusts. Read More